Have you recently discovered puzzling small red spots or bumps emerging on your arms, perhaps accompanied by an incessant itch that intensifies particularly after dark? Across the United Kingdom, a significant increase in scabies cases has been observed. Reports from the Royal College of General Practitioners (RCGP) indicate diagnosis rates exceeding the five-year average, especially prevalent in northern England. This highly contagious skin condition, caused by microscopic mites that burrow beneath the skin’s surface, can affect anyone, irrespective of their personal hygiene habits. The persistent discomfort can severely disrupt sleep and daily routines, often leading to frustration and self-consciousness. However, there’s a positive aspect: recognizing the early signs and understanding when to consult a healthcare professional can profoundly impact managing this condition. Continue reading to uncover what these itchy red spots might signify and the immediate actions you can take.
Understanding Scabies: Causes, Symptoms, and Its Recent Surge in the UK
Scabies is a prevalent skin condition initiated by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, which burrows into the outermost layer of human skin to deposit its eggs. This invasive activity triggers an allergic response from the host, manifesting as severe itching and a characteristic skin rash. Recent figures underscore a significant rise in cases throughout England, with General Practitioners observing an elevated frequency of presentations, a trend highlighted by Professor Kamila Hawthorne of the RCGP. Several elements contribute to this spread, including communal living environments like university dormitories, care facilities, or multi-person households, alongside intermittent availability of standard treatments. The National Health Service (NHS) emphasizes that scabies can affect individuals of any age or background, debunking the myth that it’s linked to poor hygiene. Instead, its primary mode of transmission is extended skin-to-skin contact. Typically, the tell-tale symptoms might not surface for 2 to 8 weeks following initial exposure, explaining how outbreaks can silently escalate before becoming widely apparent.
Identifying Scabies: Key Symptoms and the Significance of Small Red Spots
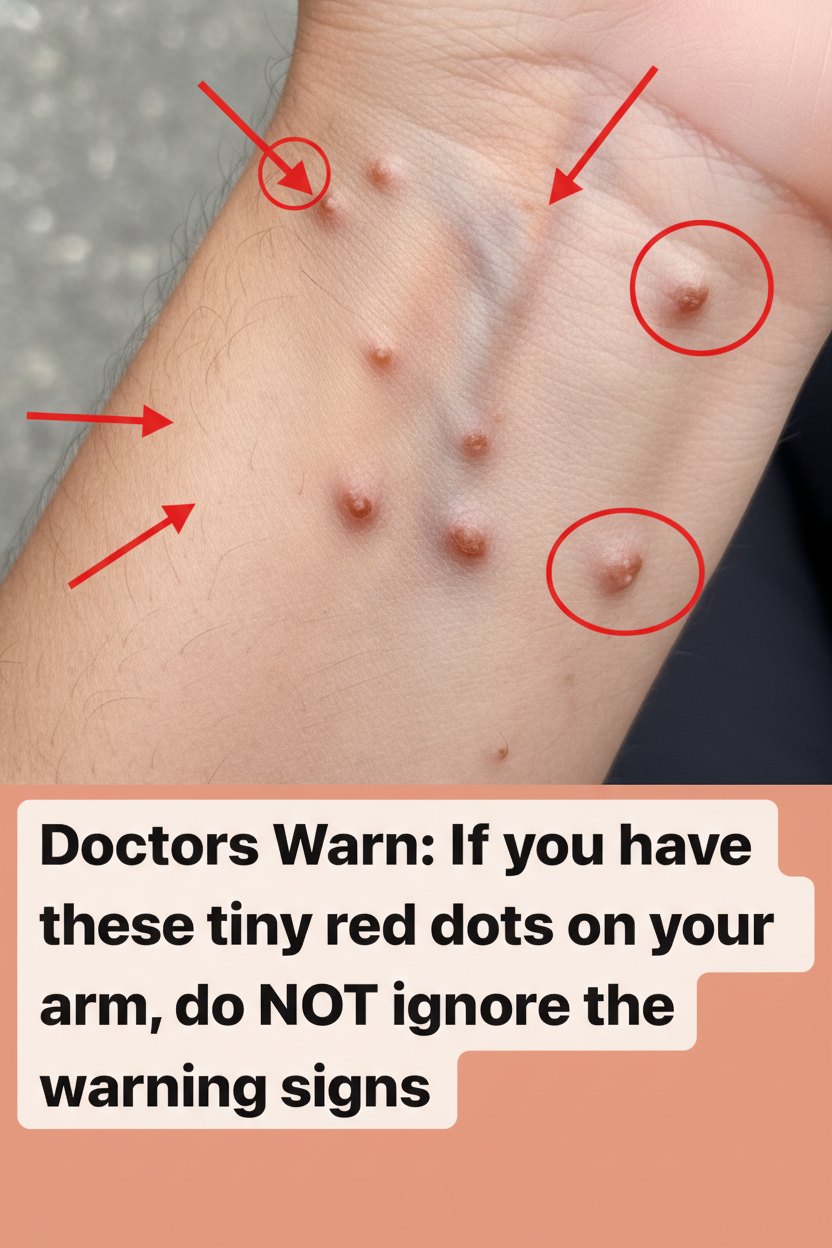
A primary and often earliest indicator of a scabies infestation is the appearance of a distinctive skin rash, characterized by small, raised spots or tiny bumps. While these are typically red on fairer skin, they might be less conspicuous on darker complexions but will still feel palpable to the touch. These characteristic itchy bumps tend to emerge in particular anatomical regions:
- Between the fingers and surrounding the wrists
- Beneath the arms or around the waistline
- Within the groin area, on the buttocks, or inside the elbows
Intense itching, especially exacerbating at night, serves as a definitive hallmark of scabies; many sufferers describe it as an unyielding and sleep-depriving sensation. Additionally, you may observe faint, wavy tracks—known as burrows—where the microscopic mites have created tunnels beneath the skin, or visible scratch marks resulting from the persistent urge to itch. However, the presentation can vary further…
For vulnerable populations, including infants, young children, older adults, or individuals with compromised immune systems, the rash might manifest on atypical body parts such as the head, neck, palms of the hands, or soles of the feet—regions typically unaffected in healthy adults. Furthermore, a particularly severe variant known as crusted scabies (or Norwegian scabies) can develop, characterized by widespread, thick, flaky crusts on areas like the elbows, knees, or hands, and is exceptionally contagious.
The Critical Importance of Not Ignoring Small Red Spots on Your Arms
Initially, those minute red dots on your arms might be dismissed as insignificant—perhaps attributed to benign irritations such as dry skin or an allergic reaction. Nevertheless, if these spots form a distinct pattern, especially when accompanied by nocturnal itching and appearing in clusters or linear formations, they could be indicative of a scabies infestation. Disregarding these warning signs risks prolonging the condition, potentially leading to increased discomfort or secondary complications like skin infections from incessant scratching. Both research and clinical experience consistently demonstrate that prompt recognition significantly curtails the spread within households and broader communities. The prevalent social stigma associated with scabies, which often causes individuals to delay seeking medical attention due to embarrassment, only exacerbates the issue, a point frequently underscored by Professor Hawthorne. Below are the common anatomical sites where scabies rashes frequently make their initial appearance:
- Wrists and between fingers: These are classic initial sites, often due to frequent hand contact.
- Arms and underarms: The presence of small red spots in these regions is a common presentation.
- Waist, groin, and buttocks: These areas are prone to infestation due to close skin-to-skin contact.
- Elbows and knees: Such areas become more prominently affected, particularly in cases of crusted scabies.
Immediate Actions: Practical Steps When Noticing Potential Scabies Symptoms
While an accurate diagnosis and subsequent treatment plan can only be provided by a qualified healthcare professional, the following practical steps are often recommended and prove beneficial when you observe these suggestive signs:
- Observe patterns closely: Meticulously track the precise locations where spots emerge and monitor any changes in the intensity or timing of the itching (for instance, if it worsens significantly in bed).
- Maintain rigorous hygiene routines: Ensure frequent hand washing and, if feasible, temporarily minimize prolonged skin-to-skin contact with others to prevent potential transmission.
- Launder items promptly and thoroughly: Hot-wash all bedding, clothing, and towels at temperatures of 60°C (140°F) or higher. This high temperature is crucial for effectively eradicating mites and their eggs.
- Avoid self-treatment without professional advice: While some over-the-counter remedies may be available, it is imperative to consult a pharmacist or General Practitioner (GP) before initiating any treatment, particularly for vulnerable individuals such as children, pregnant individuals, or those with underlying health conditions.